Note for Neural Networks (1)
ANN: Artificial neural networks
- contains neurons which kind like organic switches
Artificial neuron (activation function)
- have a “switch on” characteristic – in other words, once the input is greater than a certain value, the output should change state i.e. from 0 to 1, from -1 to 1 or from 0 to >0.
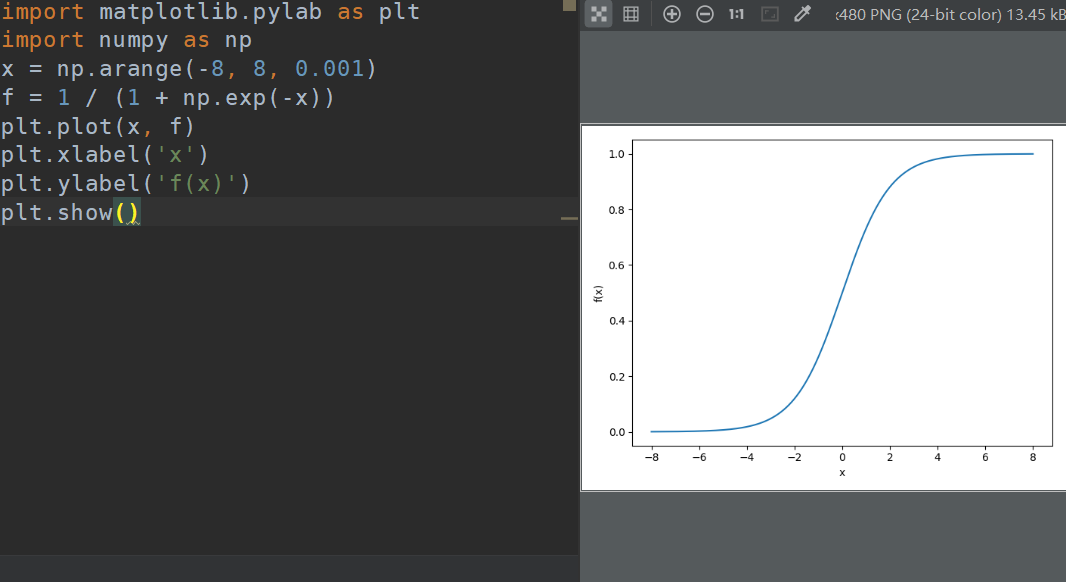
sigmoid:
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arrange(-8, 8, 0.1)
f = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
plt.plot(x, f)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.show()
Perceptron: Node
network:connected layer of nodes
input: weighted inputs
output: apply activation function to the sum of the weighted inputs
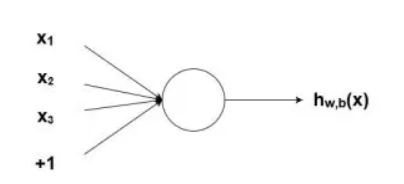
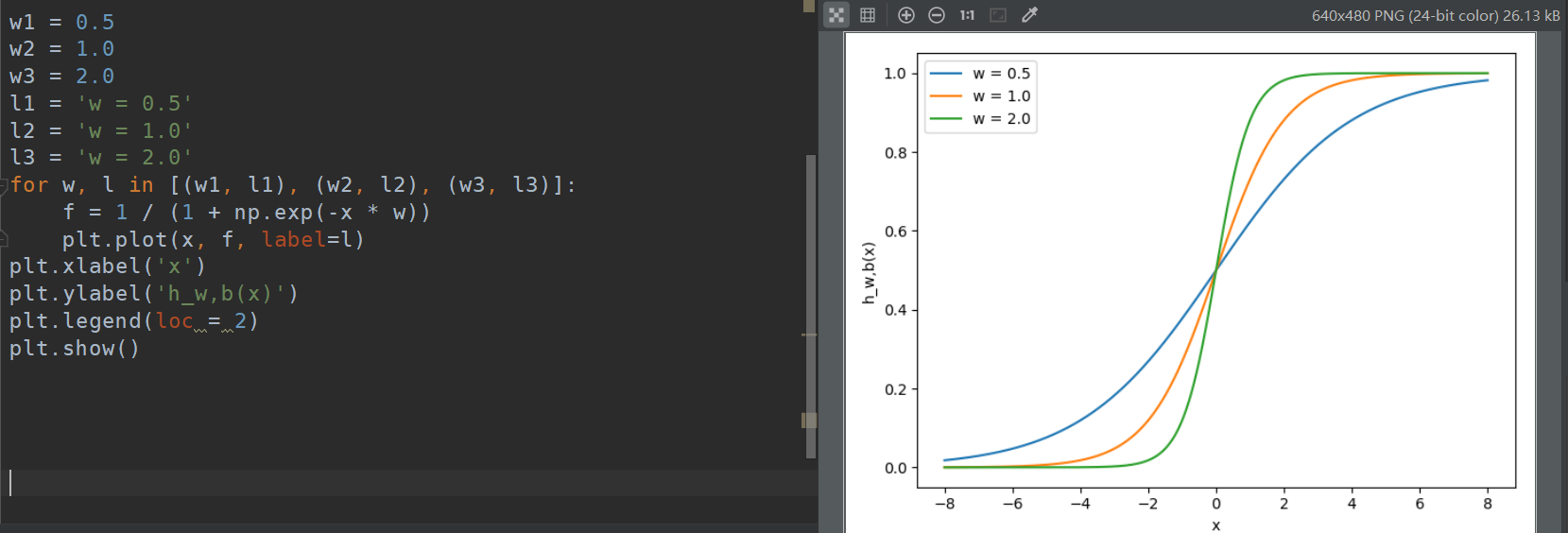
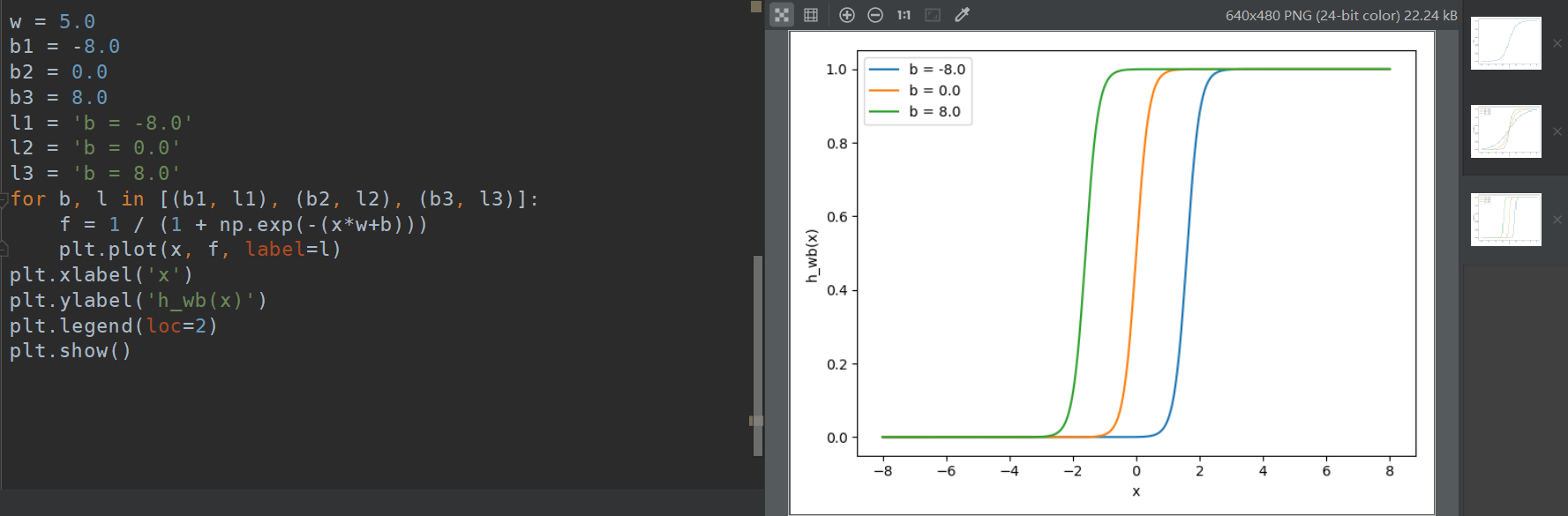
Fig: Example for $h_{w, b}(x) = x1w1$
Putting together the structure
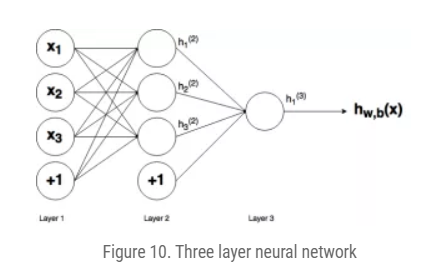
Fig: A multi-layer neural network (input(L1) + hidden(L2) + output(L3))
${w_{i, j}}^{(l)}$ $i$ refers to node number of the connection in layer $l+1$ and $j$ refers to the node number of the connection in layer $l$
For example, the connection between the first node of layer 1 and the second node of the layer 2 is $w_{21}^{(1)}$
$b_i^{(l)}$ $i$ is the node number in the layer $l+1$
For example, the weight on the connection between the bias in layer 1 and the second node in layer 2 is given by $b_2^{(1)}$
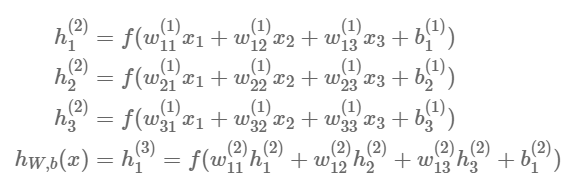
Feed-forward
Use matrix to represent the parameter:
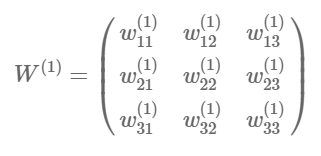
import numpy as np
w1 = np.array([[0.2, 0.2, 0.2], [0.4, 0.4, 0.4], [0.6, 0.6, 0.6]])
w2 = np.array([[0.5, 0.5, 0.5]])
b1 = np.array([0.8, 0.8, 0.8])
b2 = np.array([0.2])
def f(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def simple_looped_nn_calc(n_layers, x, w, b):
for l in range(n_layers - 1):
# Setup the input array which the weights will be multiplied by for each layer
# If it's the first layer, the input array will be the x input vector
# If it's not the first layer, the input to the next layer will be the
# output of the previous layer
if l == 0:
node_in = x
else:
node_in = h
# Setup the output array for the nodes in layer l + 1
h = np.zeros((w[l].shape[0],))
# loop through the rows of the weight array
for i in range(w[l].shape[0]):
# setup the sum inside the activation function
f_sum = 0
# loop through the columns of the weight array
for j in range(w[l].shape[1]):
f_sum += w[l][i][j] * node_in[j]
# add the bias
f_sum += b[l][i]
# finally use the activation function to calculate the
# i-th output i.e. h1, h2, h3
h[i] = f(f_sum)
return h
w = [w1, w2]
b = [b1, b2]
# a dummy x input vector
x = [1.5, 2.0, 3.0]
simple_looped_nn_calc(3, x, w, b)
Vectorization:
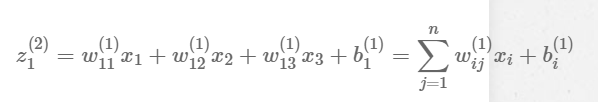
Generalization:
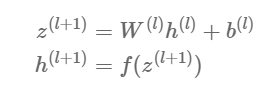
def matrix_feed_forward_calc(n_layers, x, w, b):
for l in range(n_layers-1):
if l == 0:
node_in = x
else:
node_in = h
z = w[l].dot(node_in) + b[l]
print(z)
h = f(z)
return h
Reference:
[1]. https://adventuresinmachinelearning.com/neural-networks-tutorial/